Causes and Treatments for Temporomandibular Disorders
What is the Temporomandibular Joint?

The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a joint that slides and rotates just in front of your ear, consisting of the temporal bone (side and base of the skull) and the mandible (lower jaw). Mastication (chewing) muscles connect the lower jaw to the skull, allowing you to move your jaw forward, sideways, and open and close.
The joint works properly when the lower jaw and it’s joint (both the right and left) are synchronized during movement. Temporomandibular Disorder (TMD) may occur when the jaw twists during opening, closing, or side-motion movements. These movements affect the jaw joint and the muscles that control chewing.
What is Temporomandibular Disorder?
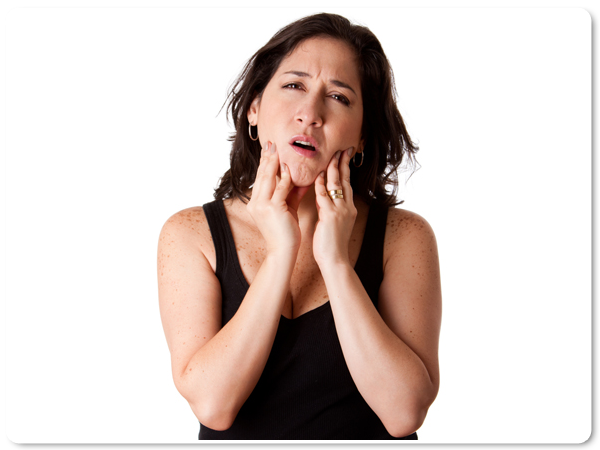
TMD describes a variety of conditions that affect jaw muscles, temporomandibular joints, and nerves associated with chronic facial pain. Symptoms may occur on one or both sides of the face, head, or jaw or develop after an injury. TMD affects more than twice as many women than men and is the most common non-dental related chronic orofacial pain.
What causes TMD?
Normal function for this muscle group includes chewing, swallowing, speech and communication. Most experts suggest that specific tasks, either mental or physical, cause or aggravate TMD, such as strenuous physical tasks or stressful situations. Most discomfort is caused by overuse of the muscles, specifically clenching or grinding teeth (bruxism).
These excessive habits tire the jaw muscles and lead to discomforts, such as headaches or neck pain. Additionally, the abnormal function can lead to worn or sensitive teeth, traumatized soft tissues, muscle soreness, jaw discomfort when eating, and temporal (side) headaches.
What TMD symptoms can I experience?
- An earache without an infection
- Jaw pain or soreness that is more prevalent in the morning or late afternoon
- Jaw pain when you chew, bite, or yawn
- Clicking when opening and closing your mouth
- Difficulty opening and closing your mouth
- A locked or stiff jaw when you talk, yawn or eat
- Sensitive teeth when no dental problems can be found
What can I do to treat TMD?
The majority of cases can be treated by unloading (resting) the joint, taking a non-aspirin pain reliever, and practicing stress management and relaxation techniques. It’s important to break bad habits to ease the symptoms. Most treatment for TMD is simple, often can be done at home, and does not need surgery. For example, control clenching or grinding during the day by sticking your tongue between your teeth. If you still experience pain, you may be grinding or clenching your teeth at night. So see your dentist for a nighttime mouthguard.
Most people will experience relief with minor treatment. More severe cases may be treated with physical therapy, ice, and hot packs, posture training, and orthopedic appliance therapy (splint). Eating soft foods and avoiding chewing gum also help relax the muscles.
Is TMD permanent?
The condition is often cyclical and may recur during times of stress, good or bad. As the patient, you should be active in your treatment, by being aware of the causes of your jaw problems after seeing a dentist for a diagnosis regime. Make routine dental appointments, so your doctor can check TMD on a regular basis.











 My husband and I love Prestonwood Dental. I already wrote a review for Dr. Daftary, and realized I should write one for her practice as well, because she and her entire team are brilliant
My husband and I love Prestonwood Dental. I already wrote a review for Dr. Daftary, and realized I should write one for her practice as well, because she and her entire team are brilliant